Spring is coming, flowers are blooming, beware of asthma attacks
[ad_1]
Asthma is one of the most common chronic respiratory diseases in the world. Due to changes in the environment and lifestyle, the number of asthma patients in my country, both adults and children, has been increasing year by year in recent years. We often see characters in movies and TV dramas die because of severe acute asthma attacks and lack of timely treatment. It can be seen that the risk of asthma is much more serious than we imagined.
How much do you know about asthma?
1) Definition of asthma: Asthma is a chronic airway inflammatory disease. The clinical manifestations are recurrent wheezing, shortness of breath, sometimes accompanied by symptoms such as chest tightness or cough. The disease is characterized by airway hyperresponsiveness and airflow. Limited reversibility, with the prolonged course of the disease or repeated attacks, the airway structure is destroyed and irreparable, that is, airway remodeling changes. Asthma is a heterogeneous disease with different clinical manifestations.
2) Causes of asthma: The incidence of asthma tends to occur in families. Research shows that the closer you are to someone with asthma, the more likely you are to develop asthma. But it does not mean that if you have a similar “asthma gene”, you will definitely have an asthma attack. In addition to the factors of susceptibility genes, the onset of asthma is also closely related to the environmental factors in which asthma-susceptible people live and work. Related.Indoor and outdoor allergens, such as dust mites, furry or smelly pets, pollen, etc., may induce asthma; some foods, such as fish, shrimp and other seafood, and eggs, milk and other allergenic foods, may also cause asthma. Predisposing factors; occupational allergens, such as paints, dyes and other chemical substances and drug factors, including air pollution, smoking, strenuous exercise, etc. caused by changes in the environment and lifestyle, may cause asthma.[1].
3) Clinical manifestations of asthma: A typical asthma attack is repeated shortness of breath, chest tightness or coughing after being exposed to stimuli of various causes. There may be auras such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. Symptoms can begin within minutes and last from hours to days, and may be relieved by taking antiasthmatic medications or by removing the irritant. Nocturnal and early morning attacks or exacerbations are typical of asthma attacks. Typical signs of an asthma attack are widespread wheezing in both lungs and prolonged expiratory sounds.
However, it is important to note that we also need to be able to recognize some atypical asthma attacks and symptoms of severe asthma. Some asthma only occurs during strenuous activities, which is easily confused with the physiological shortness of breath during exercise, which is called exercise-induced asthma. In addition, clinically there are asthma attacks without wheezing, and patients only complain that they simply cough for a long time. , and antibiotic treatment is ineffective, simple chest tightness and shortness of breath and other seemingly unrelated symptoms occur. In severe asthma attacks, patients may experience critical symptoms such as mouth breathing and profuse sweating. Moreover, when an asthma attack is severe, the auscultation is very different from a typical attack. There will be a “silent lung” phenomenon in which the wheeze in both lungs is weakened or even disappeared, which is a sign of a critical condition.
4) The pathogenesis of asthma: Chronic inflammation of the airways is a basic feature of asthma. In susceptible people, genetic factors and environmental factors trigger the interaction of airway inflammatory cells, cytokines and inflammatory mediators, causing airway nerve damage. Imbalances in regulation and structural and functional abnormalities of airway smooth muscle then lead to a “big explosion” of airway inflammation, ultimately leading to airway hyperresponsiveness, tracheal spasm, and subsequent asthma attacks.
5) Related examinations: To determine which type of respiratory disease you have, pulmonary function testing is the basis. Chronic lung diseases such as emphysema, COPD, and asthma all have symptoms of decreased lung function. Bronchial provocation test (BPT), bronchodilation test (BDT), peak respiratory flow (PEF) and its variation rate measurement are the diagnostic criteria for asthma. They meet the positive of any one of them combined with typical or atypical clinical manifestations of asthma. Asthma can be diagnosed. In patients with asthma, the eosinophil count in induced sputum culture is increased, chest imaging examination shows hyperventilation, bronchial mucus obstruction, etc., arterial blood gas analysis shows hypoxia and CO2 retention, and exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) detection, etc.
Do you underestimate your asthma?
Asthma, as a chronic disease of the respiratory system, does not only have one state of attack. The absence of asthma attacks does not mean that “everything is fine”. Clinically, asthma is divided into acute attack phase, chronic persistent phase and clinical remission phase. Understanding the stages of asthma is of great value for asthma patients to self-assess their condition and seek timely medical treatment.
Acute attack stage: occurs under the stimulation of various predisposing factors, and is divided into four levels: mild, moderate, severe and critical according to the severity.
Mild to moderate attacks are characterized by shortness of breath after activity, anxiety, accelerated respiratory rate, wheezing in the lungs, and manifestations of mild hypoxia, such as dizziness, palpitation, etc.; severe attacks include shortness of breath during rest, and extremities. Breathing while sitting, pronouncing single words when speaking, extremely anxious and irritable, sweating profusely, respiratory rate >30 times/min, often with three concave signs, loud and diffuse wheezing in the lungs can be heard even without a stethoscope, and heart rate often increases > 120 times/min, pulse odd, PaO, <60mmHg, PaCO2>45mmHg, respiratory failure, arterial partial pressure of oxygen ≤ 90%, respiratory acidosis; patients with critical illness experience drowsiness or confusion and other disturbances of consciousness, chest and abdominal contradictions Movement, that is, the chest drops when inhaling and rises when exhaling, silent lungs, slow or irregular pulse rate, severe respiratory failure and acid-base balance disorder.
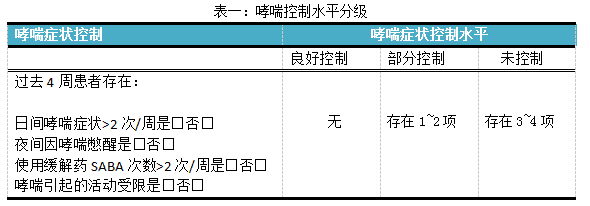
Chronic duration: patients have varying degrees of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness and other symptoms for a long period of time, which may be accompanied by decreased lung function. Currently, the most widely used method for assessing the severity of chronic persistent asthma is asthma control level. Patients can also self-assess to determine their asthma control status and future risk. See Table 1 for details.
The clinical remission period refers to the patient’s absence of wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, cough and other related symptoms for more than 1 year.[2]. If patients do not pay attention and their asthma is not well controlled, asthma will recur or worsen, which will not only affect the quality of life, but also increase the probability of complications such as pneumothorax, mediastinal emphysema, and atelectasis, and the progression of the disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and bronchitis. The risk of secondary lung diseases such as dilation and cor pulmonale is also increased.
Asthma prevention and control requires long-term persistence
At present, asthma cannot be completely cured, but cooperation between doctors and patients and long-term standardized protection and treatment can enable asthma patients to control their symptoms for a long time and prevent future risky occurrences. This is our common goal.
In actual operations, patients should follow the preventive principles of asthma: prevent before they become ill, avoid exposure to asthma triggers and allergens, and maintain a comfortable mood; prevent from existing illnesses: when there are no symptoms of asthma, early prevention should be carried out to enhance disease resistance. Prevent the progression of this disease. Prevention of relapse after illness: Effectively control asthma symptoms and prevent continuous recurrence and aggravation of adverse complications.
The main drugs used to treat asthma include controller drugs and reliever drugs, as well as additional drugs for the treatment of severe asthma. Controller drugs: Drugs that need to be used daily and maintained for a long time. They generally have an anti-inflammatory effect and are designed to reduce recurrence. Relief medicines: Also known as emergency medicines, they are usually inhaled medicines. They are used as needed when symptoms occur. They can quickly relieve asthma symptoms and control attacks.Additional therapeutic drugs for severe asthma: mainly immune preparations, with the purpose of enhancing the patient’s body function and maintaining the quality of life.[1].
In terms of specific drug use, patients should follow the guidance and selection of the doctor in charge, do preventive management of life, pay attention to individualized medication, and standardize the long-term treatment of asthma.
Give full play to the advantages of traditional Chinese medicine in treating asthma
Traditional Chinese medicine refers to asthma as wheezing disease or wheezing syndrome. As early as the Spring and Autumn Period and the Warring States Period, there are records of attack characteristics such as “wheezing” related to this disease. The occurrence of asthma syndrome is due to internal deficiency of the lungs, spleen, and kidneys, resulting in phlegm. Drinking in the lungs becomes the “root cause” of asthma syndrome. Under the stimulation of various external factors, internal and external evils combine to trigger the onset of asthma syndrome.
Traditional Chinese medicine treats asthma syndromes based on internal and external causes, and follows the principle of “treating the symptoms when an attack occurs, and treating the root cause in normal times”: 1) During the attack period, the main focus is on “eliminating phlegm”, taking into account the healthy qi, and dialectically paying special attention to the condition of cold and heat, deficiency and excess, and the transformation of both syndromes. Changes should be treated according to syndrome differentiation. If a crisis of asthma occurs, corrective measures should be taken to rescue the patient immediately. 2) During the remission period, the main focus is to strengthen the body and treat the root cause, while also taking into account the symptoms. Those with Yang Qi deficiency should be warm and nourishing, and those with Yin deficiency should be nourished. Depending on the degree of deficiency of the lungs, spleen, and kidneys, the lungs, spleen, and kidneys should be nourished, spleen, and kidneys nourished respectively. Kidney-based treatment aims to prevent and reduce recurrence by nourishing the lungs, spleen and kidneys. 3) The word “urgent” should be given priority in treatment. If the disease is long-term and the patient is deficient, there will be less evil and more deficiency at the time of onset, turbid and excessive phlegm, and symptoms such as mouth opening and shoulder lifting, nose fanning, shortness of breath, sweating, cold limbs, floating and rootless pulse, etc. For those who are in crisis of asthma or have phlegm plugs blocking the airway during an attack and suffering from severe hypoxia, they should also focus on first aid and righting, and promptly adopt modern treatments such as sputum suction or antispasmodic treatment.[3].
In addition to taking advantage of the overall treatment idea of syndrome differentiation and treatment and taking into account both the symptoms and root causes, TCM also has rich experience in prevention and care when treating asthma syndrome.During the remission period of asthma syndrome, acupuncture points on the lungs, trachea, Shenmen, adrenal glands, spleen, kidneys, etc. are used for auricular point pressing therapy, and the patient is instructed to perform breathing exercises, Tai Chi and other exercises, and to avoid eating fat, sweet, thick, and salty foods. and other stimulating factors, quitting smoking and drinking, avoiding the odor of smoke and other factors in daily life, regulating emotions, keeping a comfortable mood, and combining work and rest, etc., all help to enhance righteousness, cultivate righteousness and consolidate the foundation, “righteousness is within, evil cannot be eliminated”, Thereby reducing asthma attacks and enhancing disease resistance[4].
To sum up, whether it is Western medicine treatment or traditional Chinese medicine treatment, its therapeutic value is worthy of recognition. Giving full play to the role of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in the prevention and treatment of asthma is a guarantee for maintaining the health of patients and improving their quality of life.
references
[1]Asthma Group of the Respiratory Disease Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Bronchial Asthma (2020 Edition)[J].Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Medicine, 2020, 43(12):1023-1048.
[2]Ge Junbo, Xu Yongjian, Wang Chen, Internal Medicine. Respiratory Diseases[M].9th edition. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House: 28-35
[3]Zhang Boli, Wu Mianhua, Internal Medicine of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pulmonary Disease Syndrome[M].Tenth Edition. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, National “13th Five-Year Plan” Textbook for Higher Education in the Traditional Chinese Medicine Industry 2017.8 (Reprinted in 201911): 53-59
[4]Liu Lujiong, Jiang Chunjuan. Observation on the efficacy of acupuncture in the treatment of cough variant asthma[J]. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture, 2022, 41 (06): 548-551.
[ad_2]
Source link

![[Love Wants Sexual Happiness Series 358]Find the culprit and overcome psychogenic erectile dysfunction. Don’t let pressure affect your sexual happiness.](https://chinathenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/171111-780x420.jpg)

![[Wanqingyi Care]My health, my rights, customized medical methods in the last stage of life](https://chinathenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/ZZ1-100-780x420.jpg)
![[Kidney Transplantation Special Topic]The survival rate of transplanted kidneys is high without dialysis treatment three times a week](https://chinathenews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/1311-780x420.jpg)



