Spending 1 billion yuan in half a year, Lei Jun Li Bin followed this track and went crazy
[ad_1]
The smart car industry is rolling forward. During this period of critical change, technological confrontations are constantly emerging. “TechLab” technology laboratory will focus on the heavy technological innovation of the smart car industry. We will deeply analyze the principles of innovation behind it, trying to clear the clouds and fog, and see the next decade of smart cars.
In 2023, a brand new tens of billions track will appear – 4D millimeter wave radar.
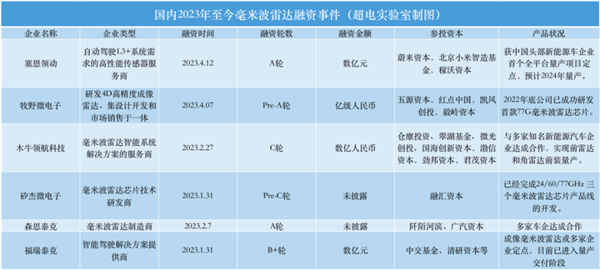
In just half a year, there have been multiple rounds of financing, and many of them are A-round or even Pre-A rounds. This market, which is still in the incubation period, has attracted many players to enter.
The latest news is that Lei Jun and Li Bin have invested in a 4D imaging radar start-up company called Sean Leading. This round of hundreds of millions of A-round financing is mainly used for 4D imaging radar mass production research and development and industrialization.
Almost at the same time, Makino Microelectronics, a company that develops 4D high-precision imaging radar, also announced the completion of the Pre-A round of financing of 100 million yuan.
According to the incomplete statistics of the Super Electric Laboratory,Since the beginning of this year, at least six 4D millimeter-wave radar companies have received financing, with a total amount of 1 billion.
Large foreign manufacturers are also deploying in this field. Traditional component giants such as Continental and Aptiv have entered the market early, and a large number of start-up technology companies have also been born, including Arbe, a supplier of Tesla’s 4D millimeter-wave imaging radar.
As intelligent driving enters the deep water area of mass production, the direction of the wind changes again and again. First, L4 is reduced to L2, and then it is infinitely close to L3. At present, the BEV architecture has become a hot focus again.
However, there is a consensus behind this, that is, multi-sensor fusion is the general trend. Even Tesla, which loves pure vision, has begun to favor 4D millimeter-wave radar. As other companies follow up, will 4D millimeter-wave radar replace lidar?
evolution super eye
Let’s first look at what is 4D millimeter wave radar.
The essence of millimeter-wave radar and lidar is to actively detect through wave signals. Since different wavelengths have different propagation characteristics, lidar is almost helpless in the face of extreme environmental weather such as rain, fog, and sandstorms, while millimeter-wave radar can continue to perform.
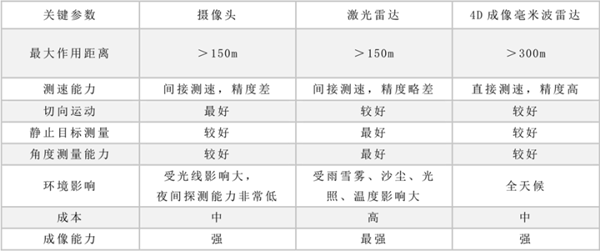
Traditional millimeter-wave radars can perceive information about obstacles in terms of distance, azimuth, and speed. It realizes the functions of distance measurement and azimuth measurement through the time-of-flight method and the Kepler effect. The millimeter-wave radar obtains two-dimensional horizontal coordinate information of distant objects by emitting electromagnetic waves of millimeter magnitude and receiving echoes.
However, due to the limitation of the antenna arrangement, the traditional vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave radar has insufficient altimetry capability, and there are great limitations in distinguishing and identifying low roadside targets, aerial targets, and static targets on the road. With the deepening of autonomous driving perception, these The short board is very obvious.
Tesla has also stated that the reason why ghost brakes appear during driving may be due to the lack of perception of millimeter-wave radar. .
Since traditional millimeter-wave radars cannot meet the requirements of car companies, ultra-high-resolution millimeter-wave radars have become the favorites of these autonomous driving companies.
The evolution history of millimeter-wave radar is actually a process of continuous improvement of the target perception dimension. In 2020, the first 4D millimeter-wave radar was born, which is the fifth-generation millimeter-wave radar.
Compared with traditional millimeter-wave radars, 4D millimeter-wave radars can not only perceive the presence or absence of targets, but also outline the targets.
This is because the 4D millimeter-wave radar is based on the traditional 3D millimeter-wave radar, adding the measurement of the pitch angle, which is the concept of “height”.

“4D” is compared with the traditional 3D millimeter-wave radar, it has information in four dimensions of range (Range), velocity (Velocity), azimuth (Azimuth), and elevation angle (Elevation), which greatly increases the ability of information perception .
This also means that from 3D millimeter-wave radar to 4D millimeter-wave radar, the most critical transformation from two-dimensional plane to three-dimensional image has been completed.
But the 4D millimeter-wave radar alone is not worth betting on by many big shots. The upgraded version of the 4D millimeter-wave radar-4D imaging radar is what the big shots are looking at.
The full name of 4D imaging radar is “4D millimeter wave imaging radar”. The key lies in the word “imaging”, which is similar to the point cloud imaging effect of lidar.
Due to the current lack of a unified definition of 4D imaging radar in the industry, “4D millimeter-wave imaging radar” is often confused with “4D millimeter-wave radar”, but the two are actually two completely different types of millimeter-wave radar.
Compared with traditional 3D millimeter-wave radar, 4D imaging radar has more than ten times the number of radio frequency transceiver channels. With the greatly improved pitch angle resolution, it can present rich point cloud images as well as distance, speed and angle of targets and environments. information.

Compared with the output measurement points of the traditional 3D radar, the 4D millimeter-wave radar has only a small increase, and the resolution of the pitch direction is low. At this time, the measurement accuracy of the pitch angle information is still not high. Therefore, 4D millimeter-wave radar still belongs to the category of spot radar in essence, and only 4D millimeter-wave imaging radar has truly completed the transformation from spot radar to imaging radar.
The popular understanding is that 4D millimeter-wave radar is still a point, but it has become denser compared with 3D millimeter-wave radar.
When the points are dense enough to a certain extent, the points in an area will form an image. At this time, the 4D millimeter-wave radar is called 4D imaging radar.
In other words, 4D millimeter-wave radar is not a 4D imaging radar in the full sense. To become a 4D imaging radar, a high-resolution point cloud is required.
Great opportunity for new players
Compared with lidar, the advantage of 4D imaging radar is lower cost.
In terms of cost, the price of lidar is more than 1,000 US dollars, while the cost of 4D millimeter-wave radar is about 1/10-1/5 of that of lidar. For example, the price of Arbe’s imaging radar is 690-1036 yuan, and the unit price of Tier 1 products such as ZF and Continental is 1036-1381 yuan.
The price of on-board lidar is tens of thousands, and the cheapest one needs to be several thousand more.
Another advantage for start-ups is that 4D millimeter-wave radar is still in the blue ocean stage, and everyone is on the same starting line.
Taking Sion as an example, this company was established in November 2021. The company is oriented towards intelligent driving, driverless driving, intelligent transportation and other intelligent connected vehicle fields, and develops environmental perception solutions suitable for L3+ and above high-performance vehicle specifications. Solutions, including 4D imaging radar intelligent hardware, sensor algorithms and software, and artificial intelligence-based perception products.
It can also be seen from its official website that it is really a start-up company. Clicking on some webpages also shows “the content of the website is under construction, so stay tuned.”
Although it is a start-up company, its background is not small. The co-founder of Sion is called Li Xuyang, who also serves as the company’s CEO.
He has studied various radar systems, radio frequency antennas and radar imaging technologies at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology for 6 years. He has personally promoted the mass production of Bosch’s L4/5 Robotaxi project multi-sensor system for nearly 7 years. time.
He once led the research and development of the fifth-generation millimeter-wave imaging radar in Bosch, Germany, and was also the person in charge of the pre-research of the sixth-generation imaging radar product.
Only one month after its establishment, Sion Leader received angel round financing, completed the development of the imaging radar A prototype in four months, and released the new imaging radar product SIR-4K developed by the company at the end of 2022.
Perhaps it was the high efficiency of Thain who led the development of products in a relatively short period of time, which made the capital of these bigwigs notice his existence.
According to Sion, the longest detection distance of SIR-4K can reach 400 meters, and the detection of static obstacles can also reach more than 150 meters. This is the ability that traditional millimeter-wave radars cannot reach before, and the angular resolution is 0.5 degrees. (horizontal) x 1 degree (vertical), which is 10 times higher than traditional millimeter-wave radar.
With 192 virtual channels, it can output 4096 point clouds, meeting the performance requirements of L3-L5 intelligent driving and driverless driving for perception
Li Xuyang, the co-founder and CEO of Sionleading, said frankly that it is indeed a bit late to enter the game. If it can enter the game one or two years earlier, the company will have a better first-mover advantage and its products will be more mature. But he believes that imaging radar The field is still a blue ocean, and new and old players gather together. Although the competition is fierce, it is a good time to make a big cake together.
The era of 4D imaging is coming
In the field of autonomous driving perception, there are mainly two technical routes. One is a purely visual route that only uses cameras as sensors for information collection, represented by Tesla.
The other is a multi-sensory fusion route that uses cameras and radars at the same time. This solution has also been adopted by most car companies.

Musk, a “pure vision” believer, has said more than once that if there is a high-resolution millimeter-wave radar, it will be better than pure vision, “but the problem is that such radar does not exist.”
Not long ago, Tesla confirmed that a high-resolution millimeter-wave radar will be used in the next car produced, which shows that Musk, who is stubborn, has to be soft in the face of increasingly accurate radar.
It is also the turn of leading companies like Tesla that makes the track of high-precision 4D millimeter-wave radar lively.
At present, there are at least 20 companies in China that have plans in the direction of 4D millimeter-wave radar, which can be mainly divided into three categories, international Tier 1, cross-border technology giants, and start-up companies.
Among them, traditional Tier 1 giants such as Bosch, Continental, Denso, and ZF were deployed earlier. A few years ago, the international millimeter-wave radar was basically dominated by these giants. The forward radar installations of these leading companies once accounted for More than 90.
In addition, Huawei-based cross-border technology giants released 4D millimeter-wave radar products in 2021, using a large array of 12T24R, which is 24 times higher than conventional millimeter-wave, capable of high resolution, and supports 4D high-density point clouds.
At that time, Miao Lijing, general manager of Radar&Camera, Huawei’s smart car solution BU fusion perception product department, said that it would become “an essential weapon for high-level autonomous driving.”
Source: WHST
Some “back waves” in China have also emerged one after another. Although they entered the game late, most of them are backed by big trees and have strong strength.
Not only is Sean Leader favored by Daxie Capital, but Geometry Partners has also received investments from Xiaomi and Baidu. Geometry Partner is based on the self-developed 4D imaging radar combined with visible light vision and infrared imaging, etc., to create an autonomous driving software and hardware integrated system of “integrated perception + intelligent decision-making”.
Furui Zhixing was also just established in 2021, but backed by the big tree of Fosun Group, its first 4D millimeter-wave radar Columbus series (Columbus) released in November last year has received fixed-point orders from domestic car companies and will be launched in 2023. Mass production will begin in the third quarter of this year.
At present, many models are equipped with 4D millimeter-wave imaging radar, such as Deep Blue SL03, Ideal L7 and other models. As intelligent driving enters into large-scale operation, the market share of 4D millimeter-wave radar will further expand, and vehicle radar will also usher in the era of 4D imaging.
[ad_2]
Source link