Please write down these food and nutrition suggestions for scientific sugar control
|
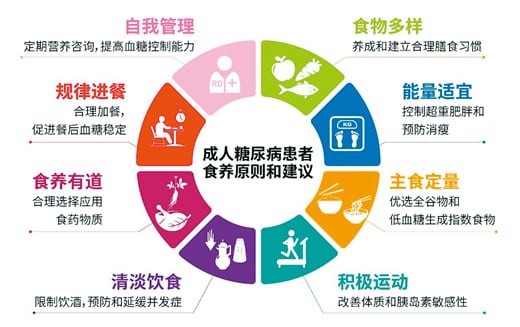
Dietary principles and recommendations for adults with diabetes. Image source: “Guidelines for Food and Nutrition for Adults with Diabetes (2023 Edition)” |
What should I eat to control blood sugar? How to eat scientifically? Recently, the National Health Commission issued the “Guidelines for Adult Diabetes Diet and Nutrition (2023 Edition)”. The guidelines give full play to the advantages of modern nutrition and traditional Chinese and Western medicine, and integrate food and medicine into a reasonable diet to help prevent and improve diabetes.
Diabetes is more related to unreasonable diet
“I didn’t expect to have diabetes at my age.” 35-year-old Xiao Zhang was diagnosed with diabetes during a physical examination not long ago. He told reporters that due to his busy work and frequent overtime work, his diet is very irregular, and he likes to eat heavy food such as high oil, high sugar, spicy, sweet and greasy, and he gained 30 catties in two years. “I also know that my lifestyle is very unhealthy, but I have always been lucky.” Xiao Zhang said that this physical examination sounded the alarm for him, and he made up his mind to correct his unhealthy lifestyle and control his blood sugar.
The “Report on Nutrition and Chronic Disease Status of Chinese Residents (2020)” shows that the prevalence of diabetes among residents aged 18 and over in my country is 11.9%, and the detection rate of pre-diabetes is 35.2%, of which type 2 diabetes is the main type. Humans have a higher prevalence. Long-term chronic hyperglycemia can cause damage to tissues and organs such as eyes, nerves, kidneys, and cardiovascular system, resulting in a series of complications, which seriously endanger human health.
In order to assist in the prevention and control of the occurrence and development of diabetes in the Chinese population, the National Health Commission organized the compilation of the “Guidelines for Diet and Nutrition for Adults with Diabetes (2023 Edition)” (hereinafter referred to as the “Guidelines”). The guidelines are mainly aimed at adults with type 2 diabetes and grassroots health workers (including nutrition instructors), and provide dietary guidance for the auxiliary prevention and improvement of diabetes. The guidelines emphasize that the risk factors for diabetes are mostly related to unreasonable diets, including long-term high-sugar, high-fat, and high-energy diets. Correcting unhealthy lifestyles, practicing reasonable diet and active exercise have always been effective means to prevent and control the occurrence and development of diabetes.
For the daily diet of diabetic patients, the guide puts forward 8 principles and suggestions: diverse food, to develop and establish reasonable dietary habits; appropriate energy, to control overweight and obesity and prevent emaciation; quantitative staple food, preferably whole grains and low glycemic index foods; Active exercise, improve physical fitness and insulin sensitivity; light diet, limit alcohol consumption, prevent and delay complications; eat well, choose and use food and drug substances reasonably; eat regularly, add meals reasonably, and promote postprandial blood sugar stability; self-management, Regular nutrition consultation to improve blood sugar control ability.
Low GI foods should account for more than 1/3 of the staple food
Dietary management and treatment are the core of blood sugar control in diabetic patients. The guidelines suggest that diabetic patients should follow the principle of a balanced diet, with a variety of foods, quantitative staple foods, rich vegetables, fruits, milk and beans, less oil, less salt, and less sugar. While controlling blood sugar, ensure adequate daily energy and adequate nutrient intake .
How to achieve a variety of food? According to the guidelines, a diverse diet should be composed of five major food groups: cereals and potatoes (including cereals, potatoes and beans), vegetables and fruits, animal foods (including livestock, poultry, fish, eggs, milk), soybeans And Nuts, Cooking Oil And Salt. The guidelines suggest that the staple food of diabetic patients should be quantified, and the main source of carbohydrates should be whole grains, various beans, vegetables, etc., and fruit should be limited; vegetables should be included in every meal, and the daily amount should reach 500 grams, of which dark vegetables account for 500 grams per day. More than half; have milk and soybeans every day, often eat fish, poultry, moderately eat eggs and livestock meat, these are good sources of protein; reduce fat intake, eat less smoked, baked, pickled and other processed meat products , Control the amount of salt, sugar and oil used.
Staple food is rich in carbohydrates, which is the core factor affecting blood sugar levels after meals. According to the guidelines, the glycemic index (GI) is a relative indicator to measure the impact of food on blood sugar. Choosing low GI foods is conducive to postprandial blood sugar control. Foods with low GI stay in the gastrointestinal tract for a long time, have a low absorption rate, and release glucose slowly. After glucose enters the blood, the peak value is low and the rate of decline is also slow. The resulting postprandial blood sugar fluctuations are relatively small, which is helpful for blood sugar control.
The guidelines suggest that diabetic patients should not eat too much staple food, and choose more whole grains and low GI foods, among which low GI foods such as whole grains and miscellaneous beans should account for more than 1/3 of the staple food. Diabetic patients with gastrointestinal diseases and elderly patients with poor digestive function can appropriately reduce the proportion of coarse grains; diabetic patients with overweight and obesity should reduce energy intake and increase activity to promote energy consumption; combined with muscle attenuation, emaciation Or malnourished patients should increase dietary energy and protein supply, combined with resistance exercise, to increase body weight.
Dietary energy is the core of weight management and blood sugar control. The guidelines suggest that the ratio of macronutrients to total energy in the dietary energy of diabetic patients is: 15%-20% of protein, 45%-60% of carbohydrate, and 20%-35% of fat. In addition, adjusting the order of meals is beneficial to control blood sugar. The guidelines suggest that diabetics develop the habit of eating vegetables first and staple food last. At the same time, it is recommended that diabetics develop a light taste. The daily consumption of cooking oil should be controlled within 25 grams, and the daily consumption of table salt should not exceed 5 grams. Pay attention to limit the intake of condiments and foods with high salt content such as soy sauce, chicken essence, monosodium glutamate, pickles, bacon, and pickles , Alcohol consumption of any kind is not recommended.
Diet based on syndrome differentiation, choose food reasonably
In addition to daily dietary recommendations, the guide also mentions the principle of TCM food nourishment centered on “syndrome differentiation and diet”. For diabetic patients with different constitutions, choosing foods with different characteristics or food and drug qualities can effectively improve the blood sugar levels of patients.
Traditional Chinese medicine believes that food has attributes such as “four qi”, “five flavors”, “meridian distribution” and “ups and downs”. “Four Qi” means that food has four different properties: cold, hot, warm, and cool. Cold and cool food can clear away heat, but easily injure yang; warm food can dispel cold, but easily injure yin. . The “five flavors” include sour, bitter, sweet, pungent, and salty. Sour taste enters the liver, bitter taste enters the heart, sweet taste enters the spleen, pungent taste enters the lungs, and salty taste enters the kidney. When nourishing food, the five flavors should be reconciled.
Traditional Chinese medicine has had the theory of “the same origin of medicine and food” since ancient times. According to the guidelines, according to the principle of TCM syndrome differentiation and treatment, food and drug substances with the effect of nourishing yin and clearing away heat should be used for yin deficiency and heat syndrome, such as mulberry leaves, cassia seeds, lotus seeds, etc. Such as mulberry, wolfberry, kudzu root, etc.; yam, poria cocos, cinnamon, etc. can be used for yin and yang deficiency. Adult diabetic patients can combine their daily diet with traditional Chinese medicine recipes. In addition, those who are known to be allergic to a certain food or drug substance, or who are taking drugs that may be contraindicated by the food or drug substance, should take it under the guidance of professionals such as physicians, licensed pharmacists, and nutritional instructors.
Effective management and stable control of blood sugar depends largely on the patient’s self-management ability. The guidelines emphasize that diabetic patients need to pay attention to and learn diabetes knowledge and self-management skills, including dietary conditioning, regular exercise, blood sugar monitoring, medication as prescribed by the doctor, insulin injection techniques, and hypoglycemia prevention and treatment.
It is worth noting that in addition to choosing the right food, it is also important to eat regularly. The guidelines emphasize that regular, regular and quantitative meals are the basis for maintaining stable blood sugar. Regular eating means that the time of three meals a day and additional meals is relatively fixed, and regular and quantitative meals can avoid overeating caused by the slow response of the satiety center caused by excessive hunger. The guidelines remind that diabetic patients should not overeat, do not eat snacks and drinks at will, but have more meals and reduce the number of meals. Whether eating at home or out, according to the individual’s physiological conditions and physical activity, the diet should be moderate and scientifically configured, with standardized and quantitative nutritional meals, reasonable planning of meal times and energy allocation to arrange meals throughout the day, and eating should be chewed slowly Pharynx, form good eating habits.
As for whether to add meals, when to add meals, and what kind of snacks to choose, the guidelines suggest that decisions should be made according to the characteristics of the patient’s specific blood sugar fluctuations. For patients with type 2 diabetes and type 1 diabetes who have a long course of disease, poor blood sugar control, and insulin injections, blood sugar monitoring should be carried out, and meals can be added appropriately according to the actual situation to prevent hypoglycemia. For thin diabetic patients and gestational diabetic patients, additional meals or snacks can also be arranged appropriately to prevent hypoglycemia, increase energy intake, and increase body weight.

![[Love Wants Sexual Happiness Series 358]Find the culprit and overcome psychogenic erectile dysfunction. Don’t let pressure affect your sexual happiness. [Love Wants Sexual Happiness Series 358]Find the culprit and overcome psychogenic erectile dysfunction. Don’t let pressure affect your sexual happiness.](https://webcdn.guangming.com.my/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/171111-780x420.jpg)
![[Wanqingyi Care]My health, my rights, customized medical methods in the last stage of life [Wanqingyi Care]My health, my rights, customized medical methods in the last stage of life](https://webcdn.guangming.com.my/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/ZZ1-100-780x420.jpg)
![[Kidney Transplantation Special Topic]The survival rate of transplanted kidneys is high without dialysis treatment three times a week [Kidney Transplantation Special Topic]The survival rate of transplanted kidneys is high without dialysis treatment three times a week](https://webcdn.guangming.com.my/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/1311-780x420.jpg)



